Which of These Describes Why a Stent Is Used
They are coated with medicine which is released into the artery over time to prevent the artery from narrowing again. Stents are used depending on certain features of the artery blockage.
Stent Purpose Procedure And Risks
Stents are used both in arteries and veins in an effort to open a narrow or closed vessel and to keep it open.

. These events are usually associated with heart attacks or episodes of angina. When angioplasty is combined with drug-eluting stent placement theres a small risk the treated artery will become clogged again. This improves blood flow to the heart muscle and relieves symptoms usually chest pain.
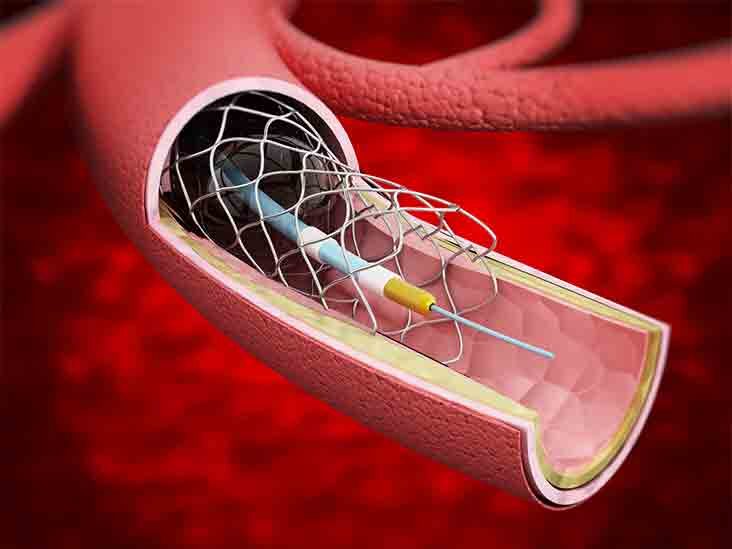
The procedure which involves a small balloon to help open the artery is done through an artery in your groin wrist or arm area. A stent is a small mesh tube that holds open passages in the body such as weak or narrow arteries. Answered by Vanish Vein and Laser Center.
While most stents are bare-metal some are coated with medication to help keep an artery open. A stent is a tiny tube that a doctor places in an artery or duct to help keep it open and restore the flow of bodily fluids in the area. A stent is a small wire mesh tube that helps prop a clogged artery open.
It helps keep your arteries -- the blood vessels that carry blood from your heart to other parts of your body. Angioplasty is minimally invasive so the recovery is. Cypher Stent is well known for being a brand of coronary stent.
The risk of re-narrowing of the artery is higher when bare-metal stents are used. Once the stent has been placed tissue will start to. - Answers A stent is used when blood vessels are clogged for example because of a plaque that has grown on the vessel wall.
This article provides a brief historical perspective of the evolution of the use of statins and stents in patients with coronary artery disease an evaluation of the available clinical data supporting the use of statins in patients undergoing PCI across a wide spectrum of clinical scenarios and a discussion of the potential mechanisms of the. Why is a stent used. Stents which are permanent are inserted through a procedure called a percutaneous coronary intervention or angioplasty.
Drug-eluting stents DES have an antiproliferative drug and a polymer that serves as the vehicle for the drug and also controls the drug release rate. Vascular access stenosis in patients undergoing chronic hemodialysis is a major issue that is associated with increased morbidity mortality and cost of medical care. Success rate is about 95 depending on the degree of narrowing of the artery.
Speak to your treating physician for more information. In certain heart disease patients use of a coronary stent reduces the. In medicine a stent is a metal or plastic tube inserted into the lumen of an anatomic vessel or duct to keep the passageway open and stenting is the placement of a stent.
Recent data have emphasized that endovascular stents could be used in the treatment of central as well as peripheral stenotic lesions. The stent helps enlarge a segment of the artery to improve blood flow which should reduce or. As with any procedure there are pros and cons associated with them.
The stent restores the flow of blood or other fluids depending on where its placed. Severe narrowing of the coronary arteries or formation of blood clots that compromises oxygen supply to the heart muscles are the common reasons why doctors use cardiac stents. A stent is a tiny tube that your doctor can insert into a blocked passageway to keep it open.
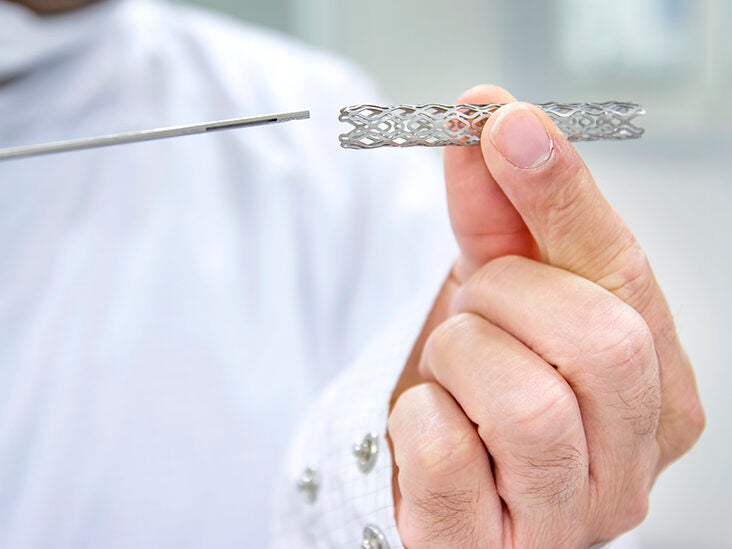
These procedures are usually done under local anesthesia. Stents without a drug coating are called bare-metal stents. A stent is a small mesh tube made of either stainless steel or cobalt chromium alloys that is placed by a catheter into a narrowed blocked coronary artery.
A stent can be made of plastic or metal or another specialized fabric. The stent stays in the artery permanently and holds it open. Different types of drug-eluting stents are coated with.
There is a wide variety of stents used for different purposes from expandable coronary vascular and biliary stents to simple plastic stents used to allow the flow of urine between kidney and bladder. These devices are used to treat blocked arteries during angioplasty and very good at preventing blockage for occurring again. This holds the artery open.
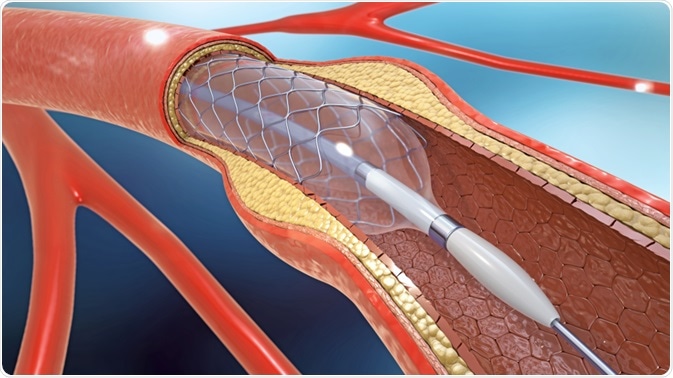
A drug-eluting stent is coated with a slow-release medication to help prevent blood clots from forming in a stent. It is put into the newly opened area of the artery to help keep the artery from narrowing or closing again. A stent is a tiny tube that can play a big role in treating your heart disease.
A stent is a small mesh tube inserted into an artery to keep it open. When the balloon is inflated the stent expands locks in place and forms a scaffold. This obstructs the flow of blood which can have.
These clots can close the artery causing a heart attack. Drug-eluting stents are the most common type of stents used in the coronary arteries. A stent is a tiny expandable metal mesh coil.
Stents help relieve blockages and treat narrow or. A stent is a small mesh tube that is inserted into a blocked section of an artery in order to keep the passageway open and allow the flow of blood to resume. Coronary stents are mesh tubes that help keep blocked arteries open.
This gives your healthcare provider options when it comes to your treatment. Blood clots can form within stents even after the procedure. Blood clotting in a stent can cause a future blockage restenosis and may lead to a heart attack.
Coronary stents are now used in nearly all angioplasty procedures. The drug inhibits excessive growth of neointima a major cause of restenosis. Bare metal stents are simple tubes made of metal mesh that can be used in both the coronary and carotid arteries.
Another advantage of angioplasty and stenting is that stents come in different sizes shapes and materials.

A Phlebography Shows Post Thrombotic Obstruction Of The Left Iliac Download Scientific Diagram
Drug Eluting Stent Alternatives

A Covered Stent Used In Aortic Coarctation Migrates Proximally During Deployment Causing Transverse Arch Obstruction Transcatheter Repositioning After One Month Sciencedirect

Transhepatic Approach For Retrograde D2 Duodenal Stent Placement New Technique And Case Series Journal Of Vascular And Interventional Radiology
Stent Purpose Procedure And Risks

Cardiology Devices Cardiology Interventional Cardiology Interventional Radiology

Radiological Stent Placement Of Post Sleeve Gastrectomy Leak Efficacy Imaging Features And Post Procedure Complications Sciencedirect

Handbook Of Interventional Radiologic Procedures Radiology Nursing Radiology Schools Interventional Radiology

Coronary Stent Positioning Under Live Ivus Guidance In Low Contrast Percutaneous Coronary Interventions The Live Ivus Stenting Technique Lichaa 2021 Catheterization And Cardiovascular Interventions Wiley Online Library

Nitinol Parts For Stents Nickel Titanium Shape Memory Alloys

Radiological Stent Placement Of Post Sleeve Gastrectomy Leak Efficacy Imaging Features And Post Procedure Complications Sciencedirect

Stents What Are Stents Nhlbi Nih

Percutaneous Coronary Intervention Pci Bupa Heart Health Information Centre Percutaneous Coronary Intervention Coronary Arteries Coronary Artery Disease

Esophageal Cancer Treatment Adult Pdq Patient Version National Cancer Institute
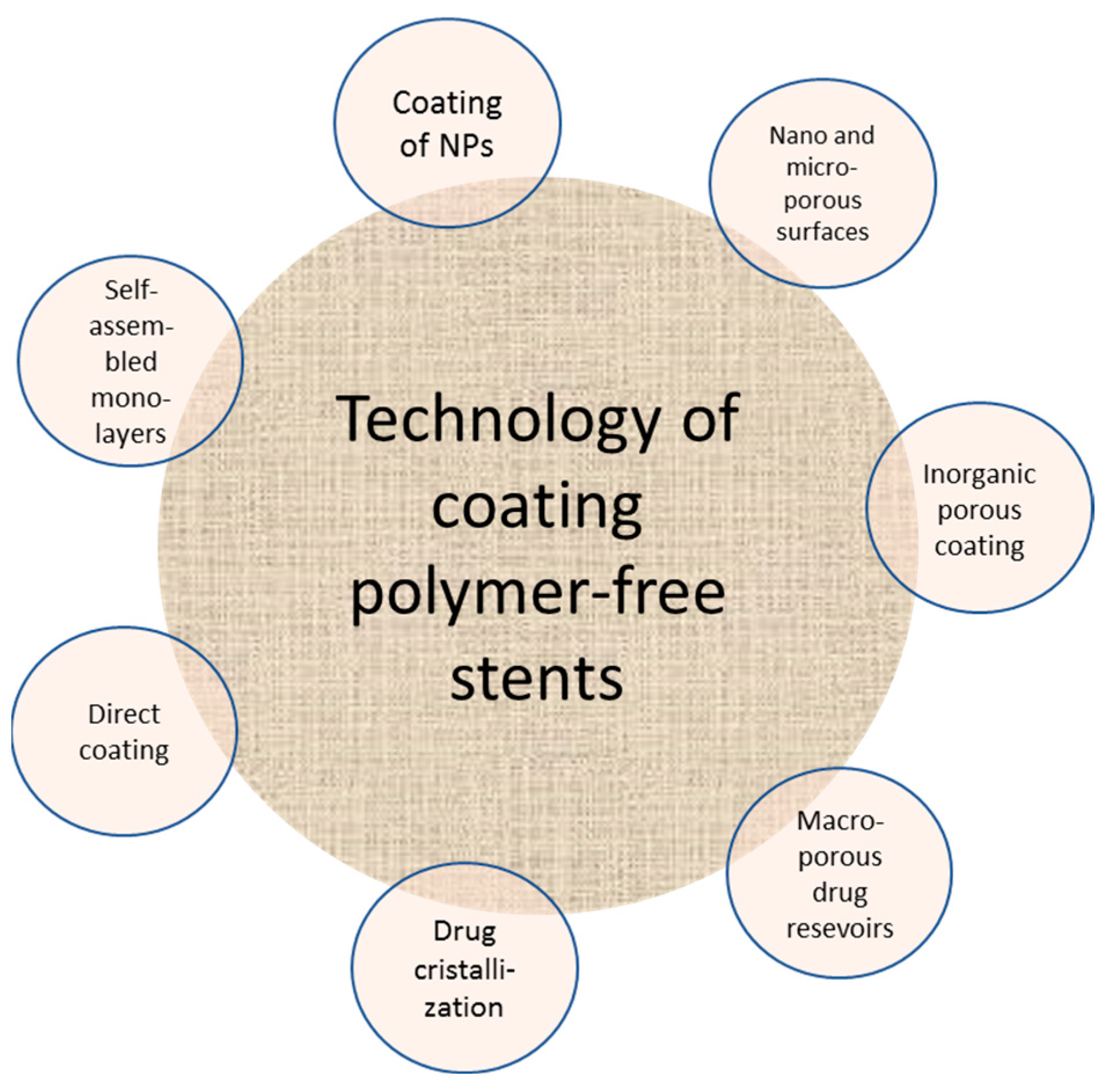
Molecules Free Full Text Drug Eluting Stents And Balloons Materials Structure Designs And Coating Techniques A Review Html
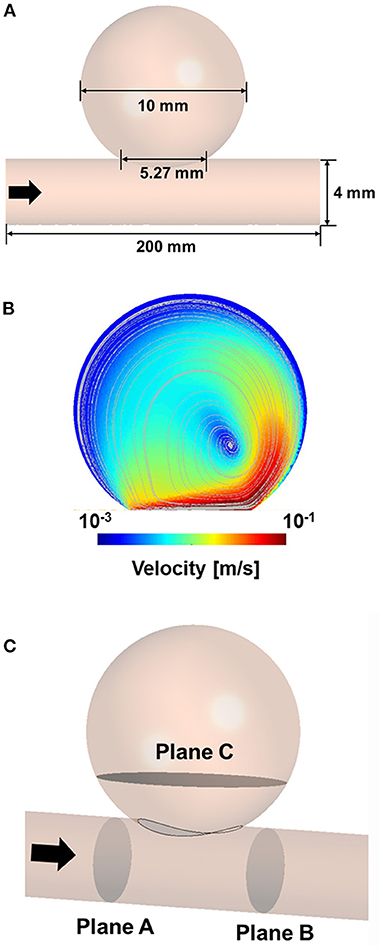
Frontiers Computational Study Of Hemodynamic Changes Induced By Overlapping And Compacting Of Stents And Flow Diverter In Cerebral Aneurysms Neurology


Comments
Post a Comment